Adjustable wrench = chiave inglese
Anti-fouling paint = vernice antivegetativa ** Necessary for ALL types of hulls.
Belt sanding = levigatrice
Blade = lama
Blade of a propeller = pala dell’elica
Bolt = bullone
Brush = spazzola
Bucket = secchio
Clamp = morsetto
Compressor = compressore
Disk sander = smerigliatrice
Distilled water = acqua distillata
Electric plane = piallatrice elettrica
Epoxy resin = resina epossidica
Fiberglass = fibre di vetro
Filler = stucco
Gel coating = finitura o strato di gel
Gelcoat = strato di gel
Glue = colla
Hammer = martello
Hand scraper = raschetto
Heat gun = fono per rimuovere vernici
Hose = tubo di gomma
Hydrochloric / muriatic acid (used to clean algae) = acido muriatico
Laminate = laminato
Mildly abrasive synthetic scratch pads = spugnette leggermente abrasive
Nail = chiodo
Nut = dado
Paint brush = pennello
Pincers = tenaglie
Pliers = pinza
Pressure washer = idropulitore
Primer = primer (prima mano di vernice)
Resin = resina
Roller = rullo
Rotary power cleaner = spazzola rotante per la rimozione di alghe, denti di cane, ecc.
Sandpaper = carta vetrata
Saw = sega
Scraper = raschietto
Screw = vite
Screwdriver = cacciavite
Scrub pads = spugne abrasive
Soft cloth = straccio soffice
Soldering torch = saldatrice a stagno
Sponge = spugna
Spray paint = vernice a spruzzo
Spray paint gun = pistola per verniciare
Stainless steel = acciaio inossidabile
Steel pads = spugna d’acciaio
Toothed spatula = spatola dentata
Treadmaster = tappetino anti-scivolo
Varnish (glossy resin coating) = vernice, lacca, smalto, trasparente, coppale
Vise = morsa
Water jet sandblaster = sabbiatrice a getto d’acqua
Wax = cera
Welding torch = saldatrice
Wire brushes = spazzola d’acciaio
Wrench = chiave
Tuesday, March 6, 2012
HELPFUL VERBS
Apply = applicare
Blister = produrre bolle
Bolt = imbullonare
Caulk = calafatare (sigillare)
Clean = pulire
Coat = coprire
Dispose of = smaltire
Dust = spolverare
Fill = riempire
Galvanize = galvanizzare
Grease = ingrassare, lubrificare
Leak = fare acqua
Mold = fare muffa
Paint = verniciare
Peel off = scrostare
Polish = lucidare
Pressure wash = idropulire
Pretreat = pretrattare
Recycle = riciclare
Remove = rimuovere
Replace = sostituire
Replank = sostituire le tavole
Reuse = riutilizzare
Rot = marcire
Rust = arrugginire
Sand = carteggiare, smerigliare
Sandblast = sabbiare
Scrape = raschiare, grattare
Screw = avvitare
Scrub = stofinare, sfregare
Seal = chiudere ermeticamente
Sharpen = affilare
Strip = sverniciare, smontare, togliere
Treat = trattare
Weld = saldare
Blister = produrre bolle
Bolt = imbullonare
Caulk = calafatare (sigillare)
Clean = pulire
Coat = coprire
Dispose of = smaltire
Dust = spolverare
Fill = riempire
Galvanize = galvanizzare
Grease = ingrassare, lubrificare
Leak = fare acqua
Mold = fare muffa
Paint = verniciare
Peel off = scrostare
Polish = lucidare
Pressure wash = idropulire
Pretreat = pretrattare
Recycle = riciclare
Remove = rimuovere
Replace = sostituire
Replank = sostituire le tavole
Reuse = riutilizzare
Rot = marcire
Rust = arrugginire
Sand = carteggiare, smerigliare
Sandblast = sabbiare
Scrape = raschiare, grattare
Screw = avvitare
Scrub = stofinare, sfregare
Seal = chiudere ermeticamente
Sharpen = affilare
Strip = sverniciare, smontare, togliere
Treat = trattare
Varnish = verniciare, laccare, smaltare, coppalare
Wash = lavareWeld = saldare
The HULL
The hull is the part of your boat that makes it float, so it must be in good condition. The material the hull is made of influences the type of maintenance it needs.
The most common materials used are:
• Wood
• Fiberglass (GRP - Glass-Reinforced Plastic = glass fiber + epoxy resins)
• Metal (steel, aluminum)
Wood – marine plywood (compensato marino), teak
Advantages (vantaggi): Natural, traditional; easy to repair
Disadvantages (svantaggi): Each type of wood needs specific care. Problems with rotting (marcire) , molding (muffa), damage from the sun and atmospheric conditions; water leakage (fare acqua) where screws (viti) are and between planks (tavole); screws can rust (arrugginire) and need to be replaced (sostituire).
Things you must do often for wood boat maintenance:
Fiberglass
Advantages: Cheap, durable, easy to maintain. Largely free of corrosion.
Disadvantages: Physical pressure, exposure to sunlight and rusty screws can cause cracking (spaccature), bumps (bozzi), bubbles (bolle) and scratches (graffi); osmosis; not fireproof (non ignifugo).
Notes: A final gel coating is usually used to protect the underlying structures and laminate. This gives it a shiny finish that needs to be cleaned (pulire) and polished (lucidare).
If the gel coat is damaged, water can get in between the coat and the laminate, which will cause the coat to peel off (scrostare). Gel coat can also be used for small repairs.
Metal – aluminum and steel
Advantages: Durable, require less work than wooden hulls
Disadvantages: Rust; in constant need of paint; bilges (stive) need careful maintenance
Aluminum
Advantages: Lightweight (leggero) and strong; easy maintenance. If it is not painted, it to an elegant gray.
Disadvantages: Maintenance is expensive because it requires special tools (atrezzature) and techniques. It is difficult to weld. Corrosion is a problem, particularly below the waterline.
Steel
Advantages: More durable and rusts less than iron (ferro).
Disadvantages: Rust is a problem, unless protected by paint.
Notes: Modern steel components are welded (saldare) or bolted (imbullonare). The hull is sandblasted (sabbiare) to have a clean surface. A zinc layer (strato di zinco) is often applied to coat (coprire) the entire hull before painting (vernicatura). Lead (piombo) paint is usually used. A hammer (martello) is used to remove large patches of rust (incrostazioni di ruggine).
Maintenance work for steel and wooden hulls is very similar. Like wood, most have a finishing layer of paint.
The most common materials used are:
• Wood
• Fiberglass (GRP - Glass-Reinforced Plastic = glass fiber + epoxy resins)
• Metal (steel, aluminum)
Wood – marine plywood (compensato marino), teak
Advantages (vantaggi): Natural, traditional; easy to repair
Disadvantages (svantaggi): Each type of wood needs specific care. Problems with rotting (marcire) , molding (muffa), damage from the sun and atmospheric conditions; water leakage (fare acqua) where screws (viti) are and between planks (tavole); screws can rust (arrugginire) and need to be replaced (sostituire).
Things you must do often for wood boat maintenance:
- sand (sabbiare)
- replace rusted metal objects
- fill (riempire) holes
- revarnish (riverniciare)
- repaint (ripitturare)
- apply anti-fouling paint on the underwater body (applicare anitivegetitivo nel pescaggio)
Fiberglass
Advantages: Cheap, durable, easy to maintain. Largely free of corrosion.
Disadvantages: Physical pressure, exposure to sunlight and rusty screws can cause cracking (spaccature), bumps (bozzi), bubbles (bolle) and scratches (graffi); osmosis; not fireproof (non ignifugo).
Notes: A final gel coating is usually used to protect the underlying structures and laminate. This gives it a shiny finish that needs to be cleaned (pulire) and polished (lucidare).
If the gel coat is damaged, water can get in between the coat and the laminate, which will cause the coat to peel off (scrostare). Gel coat can also be used for small repairs.
Metal – aluminum and steel
Advantages: Durable, require less work than wooden hulls
Disadvantages: Rust; in constant need of paint; bilges (stive) need careful maintenance
Aluminum
Advantages: Lightweight (leggero) and strong; easy maintenance. If it is not painted, it to an elegant gray.
Disadvantages: Maintenance is expensive because it requires special tools (atrezzature) and techniques. It is difficult to weld. Corrosion is a problem, particularly below the waterline.
Steel
Advantages: More durable and rusts less than iron (ferro).
Disadvantages: Rust is a problem, unless protected by paint.
Notes: Modern steel components are welded (saldare) or bolted (imbullonare). The hull is sandblasted (sabbiare) to have a clean surface. A zinc layer (strato di zinco) is often applied to coat (coprire) the entire hull before painting (vernicatura). Lead (piombo) paint is usually used. A hammer (martello) is used to remove large patches of rust (incrostazioni di ruggine).
Maintenance work for steel and wooden hulls is very similar. Like wood, most have a finishing layer of paint.
Sunday, March 4, 2012
Types and Parts of Boats
Boats come in many styles and shapes, but the names of the different parts are the same. These are the most important terms.
Recreational Boat / Motor Boat
Recreational Boat / Motor Boat
Front view:
- Beam - Maximum width of a vessel
- Freeboard: Distance from water to lowest point of the boat where water could come on board
- Draft: Depth of water needed to float a vessel
- Propeller: Rotates and powers a boat forward or backward
- Keel: Main centerline (backbone) of a vessel or the extension of hull that increases stability in the water
- ******************* Other terms you should know. *****************
Fishing boat /
Rubber Dinghy Ferry Boat
Hydrofoil
Main Types of Boats
Barge
= chiatta
Canoe
= canoa
Catamaran
= catamarano
Cruise
ship = nave da crociera
Ferry
= traghetto
Fishing
boat = barca da pesca
Hydrofoil
= aliscafo
Lifeboat
= scialuppa di salvataggio
Mercantile
ship = nave mercantile
Patrol boat = motovedetta
Patrol boat = motovedetta
Recreational
/ pleasure boat = barca di diporto
Row
boat = barca a remi
Rubber
dinghy = gommone
Sailboat = barca a vela
Sailboat = barca a vela
Trawler
(fishing boat with net) = peschereccio
(per la pesca a strascico)
Tugboat = rimorchiatore
Tugboat = rimorchiatore
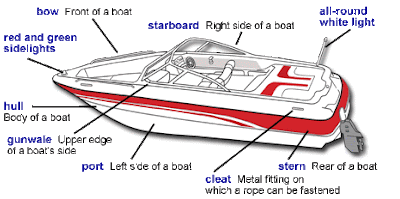
Parts of a Boat/Ship
All-round white
light = luce di coronamento (a poppa)
Beam
= larghezza/lunghezza fuori tutto
Bearing
= mozzo meccanico
Bilge
= sentina
Bitt
/ Bollard = bitta (grandi barche: dove si
attacca la cima)
Bow = prua (davanti / forward)
Bulkhead = paratia
Cleat
= galloccia (piccole barche: dove si
attacca la cima)
Deck
= ponte
Draft / underwater body = pescaggio /opera viva
Freeboard / top side = bordo libero / parte superiore /opera morta
Gunwale
= capo di banda (bordino superiore della
murata)
Hold = stiva
Hull = scafo
Keel = chiglia
Mooring
= ormeggio (posto)
Moorings
= ormeggi (cime)
Outboard
motor = motore fuori bordo
Port = sinistra (parte sinistra della nave)
Propeller = elica propulsore
Propeller
shaft = asse dell’elica o albero ruotante
Red and green lights = luci di via
Rudder = timone
Rudder
blade = pala del timone
Rudder
shaft = asse del timone
Seacock = presa a mare
Shaft seal = sigillo fra la pala e l’asse del timone
Shaft seal = sigillo fra la pala e l’asse del timone
Starboard = dritta (parte destra della nave)
Steering
quadrant = quadrante dello sterzo
Stern = poppa (dietro / aft)
Strut
= braccio
Transom
= specchio di poppa
Waterline = linea di galleggiamento
Wheel
/ helm = ruota del timone
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)